This article throws light on almost all things about BLDC motors.
Working principle, types, advantages, and more are being described in this article. So let’s take a closer look at each of them.
WHAT IS BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR?
A brushless DC electric motor (BLDC) is an electric motor driven by a DC voltage supply and electronically commutated instead of brushes as in traditional DC motors. BLDC motors are more popular today than traditional DC motors, but development of this type of motor was not possible until the 1960s, when solid-state electronics were developed.
FUNCTIONAL PRINCIPLE OF THE BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR
The BLDC motor works according to a principle similar to that of a brushed DC motor. Lorentzsche’s law of force, which states that whenever a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force. As a result of the reaction force, the magnet experiences an equal and opposite force. In the BLDC motor, the current-carrying conductor is stationary and the permanent magnet moves. When the stator coils are energized by the source, becomes an electromagnet and starts creating the uniform field in the air gap.
Although the supply source is DC, the switching produces a trapezoidal AC voltage waveform. Due to the interaction force between the stator of the electromagnet and the rotor of the permanent magnet, the rotor continues to rotate. With the switching of the windings as a high and low signal, the corresponding winding is energized as the north and South Pole. The permanent magnet rotor with north and south poles is aligned with the stator poles, causing the motor to rotate.
TYPES OF BRUSHLESS DC MOTORS
There are different types of brushless DC motors. They are classified relying on design, sort of parts, power signal, and other criteria. Different types of devices offer different benefits and are therefore used in a variety of applications. Here, I will take a detailed look at the types of brushless DC motors used today. I’ll also examine the pros and cons of each type based on parameters like torque, speed, and efficiency.
COMMON TYPES OF BRUSHLESS DC MOTORS
Various types of BLDC motors are used in different environments, such as: B. in electrical industrial machines and electronically. Household appliances, vehicles and robotic devices.
TYPES OF BRUSHLESS DC MOTORS CAN BE CLASSIFIED AS FOLLOWS.
- Based on design
- Internal brushless DC motor (also called inner rotor)
- External brushless DC motor (also called outer rotor)
- Based on using sensor
- Brushless DC motor with sensor
- Brushless sensorless DC motor
- Based on number of poles
- Single-pole brushless DC motor
- Multi-pole Brushless DC Motor
- Based on Power Signal Type
- Brushless Sine Wave DC Motor
- Trapezoidal Brushless DC Motor
The types of BLDC motors are explained as follows.
IN-RUNNER BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR
This type of BLDC motor has the rotating part (rotor) in a set of electromagnetic coils (stator). This design of the brushless DC motor allows for heat dissipation by conduction, since the stator coils are mounted on the motor case. A built-in brushless DC motor easily achieves top speeds and is best suited for applications that require higher speed characteristics. These motors often do not use many poles on the rotor. This reduces its performance at lower speeds.
OUT-RUNNER BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR
This BLDC output motor is basically the opposite of the input type. Also called an outer rotor BL motor, it uses an outer casing that rotates around a stationary inner part. Out runner BLDC motors generally use a larger number of permanent magnet poles on the rotor. That means more torque and smoother running. The main disadvantage of the brushless DC out runner motor is its low speed. As a result, these motor types are better suited for high torque, low speed applications.
SENSORED BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR
A sensored brushless DC motor relies on sensors to provide rotor position data. These types of BL motors offer reliable performance at lower speeds. At lower speeds, the sensors provide accurate data to enable smooth rotation. The main disadvantage of motors with sensors occurs at higher speeds, when sensor feedback becomes unreliable. Adverse conditions such as dusty environments or high temperatures also affect the sensors and thus the operation of the engine. These motors are better suited for low speed applications.
SENSORLESS BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR
This type of motor does not use sensors. Instead, the controller relies on the back emf generated in the stator coils to calculate the position of the rotor. These sorts of brushless DC motors provides the best performance at high speeds.
You can also use them in harsh environments because they don’t use sensors. Its error becomes apparent at low speeds when the back EMF is too low to be read by the controller or when starting from a steady state situation. These motor types are suitable for low cost, high speed applications and harsh conditions.
SINGLE POLE BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR
A single pole uses a rotor made up of a single pair of poles, North and South. This kind of brushless DC motor design has its advantages and disadvantages.
Starting with the power, the engine can reach extremely high speeds. On the other hand, at low speeds, the performance of unipolar motors drops significantly, which affects stability and rotational efficiency. Therefore, they are best used in high-speed applications.
MULTI-POLE BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR
Multi-pole motors use multiple poles on the rotor, most commonly up to eight. As mentioned above, these are placed with the opposite poles facing each other. More rods provide smoother rotation, but at the expense of speed. As a result, these types of BL motors do not reach high speeds and are mainly used in low speed applications that require high torque.
OTHER TYPES OF BRUSHLESS DC MOTORS
It is common to group brushless DC motors by their power and back EMF voltage signals. Engines in this category are discussed below.
Trapezoidal Brushless DC Motor: A trapezoidal BLDC motor uses a current signal that forms a trapezoidal shape. This is a simple switching method compared to the sine wave type. The method is to power one pair of terminals at a time while leaving the third terminal unconnected. A disadvantage of the signal, despite its simplicity, is the torque ripple effect it causes. This makes the engine run less smooth, especially at low speeds. At higher speeds, these motors perform better than sinusoidal types and are suitable for applications where high speeds are primarily used.
Sinusoidal Brushless DC Motor: These types of brushless DC motors use a duty cycle signal that forms a sine wave. With this switching method, the controller attempts to power all the stator windings and uses a current that follows a smooth sine wave. The result is a cancellation of the torque domino effect common to trapezoidal motors. A sinusoidal BLDC motor offers smooth performance, but mainly at lower speeds. At high speeds, the torque is reduced. Therefore, you will find that they are better suited to low-speed situations.
ADVANTAGES OF THE BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR
- Less general maintenance due to the lack of brushes.
- Small size with much superior thermal properties.
- Greater speed range and less electrical noise.
- It has no mechanical switch or related problems.
- High efficiency and high power-to-size ratio by using a permanent magnet rotor.
- High operating speed even under load and unload conditions due to the absence of speed-limiting brushes.
- Smaller motor geometry and lighter weight than DC brushed motors and AC induction motors.
- Long service life as no inspection or maintenance of the switch system is required.
- Higher dynamics due to low inertia and carrier windings in the stator.
- Less electromagnetic interference.
- Low noise level due to the absence of brushes.
BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR VS. BRUSH DC MOTOR
A brushless motor differs from a brush motor in a number of ways, including design, operation, and components. These differences, in turn, affect engine performance and durability in different ways. So that you can quickly understand the differences, I have broken down the comparisons according to the characteristics mentioned and other parameters.
Construction: A brushless motor will utilize electromagnets for the stator and permanent magnets for the rotor. A brushed motor does the opposite, with rotating coils forming the rotor and a permanent magnet forming the stator.
Commutation Method: A brushed motor uses brushes and a mechanical commutator. The brushless DC motor commutator is electronic and based on solid state electronics. Torque at
different speed levels. Brushed motors experience a slight loss of torque at higher speeds.
Control: BLDC motors rely on electronic control to function. Brushed motors don’t need it unless running at variable speed.
Noise level: Brushed motors generate more noise than BL motors, mainly due to the mechanical action of the brushes on the commutator. The noise of the brushless DC motor is always very low because fewer mechanical parts are used.
Maintenance Requirements: Compared to brushed types, brushless DC motors are low-maintenance devices because they do not use wearing parts such as brushes and commutators.
Efficiency: DC brushless motor efficiency is usually much higher than brushed motor, up to 85%-90%. This is due to the lack of brushes, low energy losses and low heat during work. Brushed motors typically achieve 75% to 80% efficiency.
Sensors: Most brushless motors use sensors to detect the position of the rotor, and some work without sensors. A brushed motor does not require a sensor.
Power Consumption: Brushless motors operate on a duty cycle signal, which significantly reduces their power consumption. Brushed motors, on the other hand, maintain a constant current flow and are not suitable for applications that require energy conservation or where overheating is an issue.
Cost: The cost of building a brushless DC motor is generally high compared to traditional brush types. This is mainly due to the inclusion of expensive electronic control circuitry and sometimes sensors.
Lifespan: Brushless motors are maintenance-free devices that last a long time. Brushed motors, on the other hand, contain parts that require regular maintenance and wear out too quickly.
Summarizing the comparison between brushless and brushed DC motor types, it is clearthat brushless motors offer more advantages. In applications where brushed motors are preferred, advantages include low cost and the ability to operate in harsh conditions.
UNITED STAR’S BLDC MOTOR FAN
If you are considering to buy a BLDC motor fan, fan factory UnitedStar’s, then, will be your first choice for the 16 Inch 12V BLDC Table Solar Fan for Home LED Light(USDC-418)!
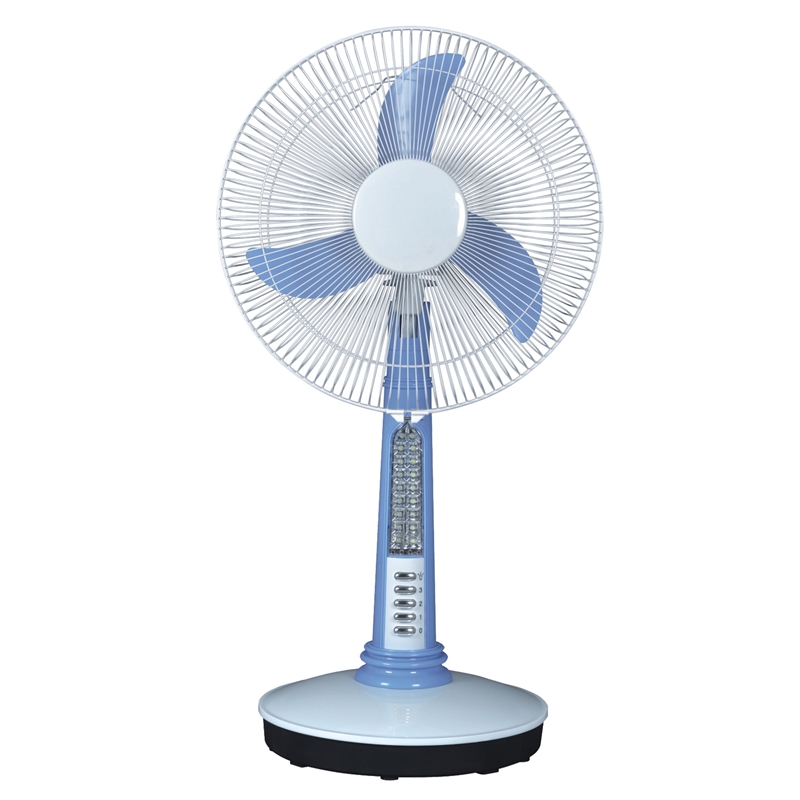

The 16 Inch 12V BLDC Table Solar Fan for Home LED Light is a great way to keep your home cool and comfortable during the summer months. This powerful and energy-efficient fan can be placed on any table or surface in your home, and it will provide a refreshing breeze to help keep you cool and comfortable. The fan’s blades are made of durable and strong materials, and the fan itself is encased in a sleek and modern design. The fan runs quietly and smoothly, making it a great addition to any home.
Solar Fan for Home available here for you to wholesale. As a BLDC table fan manufacturer in China, we do hard work to be a reliable well-built fan wholesale to offer performance products and best quality customer service with our clients.
In addition to solar fan in our stock, we also offer custom made service, feel free to contact us for any custom made needs.


